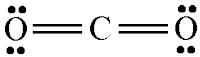Organic Chemistry is a branch of chemistry there studies structure, composition,
reactions, properties and synthesis of organic compounds and organic materials, Organic compounds those compounds which have
carbon and hydrogen, and may contain any number of other elements.
We will Explain Each and Everything
in Easy and Better Way to Understand The Organic Chemistry:-
a) How do the Chemical Bonds
Break?
b) Why do Chemical Bonds Break?
c) What will be the Products?
d) How will Reaction be done?
First of all let's discuss about Carbon atom:-
Carbon is a Chemical Element with
the Symbol C and Atomic
Number is 6. It is non-metallic and tetravalent which is making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds.
1.
Carbon has four valences.
2. Carbon has a property
of catenation. It can make a large chain with addition of other carbons.
3.
A carbon can form
single, double or triple bond.
4.
For a carbon atom, it
is not possible to make more than 3 bonds with adjacent carbon atom because a
carbon atom complete its octet from overlapping which consists directional
property.
Lewis Structure of Carbon
Tetravalency:-
Carbon being tetravalent, is capable of bonding with four
other C atoms or some other monovalent atoms. Carbon can form compound with
oxygen, hydrogen, chlorine, sulphur, nitrogen and phosphorus. These compounds
have specific properties depending upon the nature of the element or group
attached with the carbon.
Chemical bond
The reactions in organic chemistry happen by the Formations and Breaking of chemical bonds.
Formation of chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances where atoms have
tendency to arrange themselves in the most stable patterns, which means that
they fill their outermost electron orbits. The attraction force of
atoms to each other through sharing, as well as exchanging, of electrons or
electrostatic forces that holds atoms together in collections known as molecules is
referred to as a chemical bond.
How the bond formation occurs......?
Types of bonds:- There are mainly 4
types of chemical bonds which are formed by atoms or molecules.
a) Covalent Bonds
b) Ionic Bonds
c) Hydrogen Bonds
d) Polar Bonds
Covalent Bonds Formation :-
Covalent bond in which one or more pairs
of electrons are shared by two atoms. This bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of elements
close to each other in the periodic table
a) Same Atoms H2, Cl2, O2
 |
Image
source: By DynaBlast CC
BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia
Commons
|
Types of covalent
bond:-
There are mainly three types of
covalent bonds, Depending upon the number of shared electron pairs
1.
Single
Covalent Bond
2.
Double
Covalent Bond
3.
Triple
Covalent Bond
Single Covalent Bond :-
HBr and CH4
Hydrogen and Bromide share one electron to each other and make a
single covalent bond.
Double
Covalent Bond :- In Ethylene,
each carbon atom shares two of its valence electron with two hydrogen atoms and
remaining two electrons with the other carbon atom. So there is a double bond
between the carbon atoms.
Triple
Covalent Bond :- Triple Covalent bond is formed
when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating
atoms i.e. Acetylene, Nitrogen.
Ionic Bonds
Formation:-
Ionic
bonding is a type of chemical bond in which one
or more valence electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another
atom, resulting in Cations and Anions which attract each other by electrostatic forces between two
ions of opposite charge.
The Question is why the atoms or molecules lose and gain the valence electron...?
Because Both atoms or molecules have to complete their octets
by losing and gaining the valency electrons for stability and electron shells
will be energetically stable.
Cations:- A cation is an atom or a molecule which is positively charged, i.e. has more number of protons than electrons. example Iron (Fe2+), Zinc(Zn2+), sodium (Na+) etc.
Anions:- An anion is an atom or a molecule
which is negatively charged, i.e. has more number of electrons than protons.
example chloride (Cl-),fluoride (F-), iodide (I-), sulfide
(S2-), etc.
Hydrogen Bond:-
A hydrogen bond(abbreviated H-bond) is a electrostatic attraction between a
hydrogen atom attached to relatively electronegative atom such
as Nitrogen, Oxygen, fluorine. it attracts the shared pair of
electrons more and so this end of the molecules becomes slightly negative while
the other end becomes slightly positive. The negative end of one molecule
attracts the positive end of the other and as a result, a weak bond is formed
between them. This bond is called the hydrogen bond(1).
same as Alcohol molecules form hydrogen bond
Polar Bonds :-
A polar bond is a covalent bond between two non-metal
atoms having different Electronegativities where the electrons forming
the bond are unequally distributed in the molecule. This causes the
molecule to have a slight electrical dipole moment where one end is slightly
positive charge and the other end is slightly negative charge such as Trigonal Planar: BF3